Unlocking the Potential: Exploring the Synergy of Artificial Intelligence and Deep Learning
Artificial Intelligence and Deep Learning: Shaping the Future
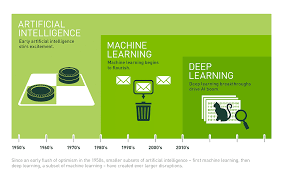
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has rapidly evolved from a niche field of study to a cornerstone of modern technology. Among the various branches of AI, deep learning stands out as one of the most transformative. This article explores the relationship between AI and deep learning, highlighting their impact on our world.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence
AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and learn like humans. It encompasses a wide range of capabilities, from simple rule-based systems to complex neural networks that mimic human cognition. AI is used in various applications, including natural language processing, robotics, and predictive analytics.
The Rise of Deep Learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses neural networks with multiple layers—often referred to as deep neural networks. These layers allow the system to learn representations of data with increasing levels of abstraction. Inspired by the human brain’s structure, deep learning models are particularly effective in recognising patterns and making predictions based on large datasets.
Key Components of Deep Learning
- Neural Networks: Composed of interconnected nodes or neurons, these networks process data through weighted connections.
- Layers: Each layer transforms the input data into more abstract representations.
- Backpropagation: A method used for training neural networks by adjusting weights based on errors in predictions.
The Impact on Industries
The integration of AI and deep learning has revolutionised numerous industries:
- Healthcare: AI systems assist in diagnosing diseases more accurately and developing personalised treatment plans.
- Automotive: Autonomous vehicles rely heavily on AI for navigation and decision-making processes.
- E-commerce: Recommendation engines powered by AI enhance customer experience by suggesting products tailored to individual preferences.
The Challenges Ahead
Despite its potential, deep learning faces several challenges. The requirement for vast amounts of data can be prohibitive, while ensuring data privacy remains a critical concern. Additionally, the “black box” nature of some models makes it difficult to interpret how decisions are made.
The Future Outlook
The future holds immense potential for AI and deep learning as research continues to advance these technologies. With ongoing improvements in computational power and algorithmic efficiency, we can expect even more sophisticated applications that will further integrate into our daily lives.
The journey towards fully-realised artificial intelligence is still unfolding. As we navigate this path, it is crucial for researchers, policymakers, and society at large to address ethical considerations while harnessing AI’s transformative power responsibly.
Five Key Benefits of Artificial Intelligence and Deep Learning: From Enhanced Efficiency to Medical Advancements
- Enhanced Efficiency
- Improved Decision-Making
- Personalised Experiences
- Medical Advancements
- Predictive Capabilities
Challenges of Artificial Intelligence and Deep Learning: Privacy, Bias, Transparency, Data Quality, and Ethics
- Data Privacy Concerns
- Bias and Fairness Issues
- Lack of Transparency
- Dependency on Data Quality
- Ethical Dilemmas
Enhanced Efficiency
Artificial intelligence and deep learning have revolutionised the way businesses operate by significantly enhancing efficiency. Through the automation of repetitive tasks, AI systems can handle mundane and time-consuming activities with remarkable speed and accuracy. This automation not only reduces the potential for human error but also frees up valuable time for employees to focus on more strategic and creative tasks. As a result, organisations experience increased productivity, allowing them to allocate resources more effectively and respond swiftly to market demands. By streamlining operations, AI and deep learning technologies enable companies to achieve greater outputs with fewer inputs, ultimately driving innovation and competitiveness in various industries.
Improved Decision-Making
One significant advantage of artificial intelligence and deep learning is their ability to enhance decision-making processes through the rapid and precise analysis of extensive data sets. Deep learning models excel at processing large volumes of information efficiently, enabling organisations to make informed decisions based on valuable insights derived from complex data patterns. This capability not only streamlines decision-making but also improves the accuracy and effectiveness of strategic choices, ultimately leading to more successful outcomes across various industries and sectors.
Personalised Experiences
Artificial intelligence and deep learning have revolutionised the way personalised experiences are crafted across various industries. By analysing vast amounts of data, AI systems can discern individual preferences and behaviours, enabling businesses to offer tailored recommendations that resonate with each user. In the realm of e-commerce, for instance, AI-powered recommendation engines suggest products based on past purchases and browsing history, enhancing customer satisfaction and engagement. Similarly, in the entertainment industry, streaming services utilise AI to curate content that aligns with viewers’ tastes, ensuring a more enjoyable viewing experience. This level of personalisation not only improves user satisfaction but also fosters loyalty by making interactions more relevant and meaningful.
Medical Advancements
Medical Advancements: The integration of deep learning in healthcare has the potential to revolutionise diagnostics, treatment planning, and patient care. By leveraging the power of artificial intelligence, healthcare professionals can access advanced tools that enhance accuracy in disease diagnosis, personalise treatment strategies based on individual patient data, and improve overall patient outcomes. Deep learning algorithms can analyse vast amounts of medical data quickly and efficiently, providing valuable insights that can lead to earlier detection of diseases, more effective treatment plans, and ultimately, better quality of care for patients.
Predictive Capabilities
Artificial intelligence and deep learning have significantly enhanced predictive capabilities, allowing businesses to forecast trends, behaviours, and outcomes with remarkable accuracy. By analysing vast amounts of historical data, AI algorithms can identify patterns and correlations that may not be immediately apparent to human analysts. This ability to anticipate future events enables companies to make informed decisions, optimise operations, and strategically plan for upcoming challenges. Whether it’s predicting consumer demand, identifying potential market shifts, or foreseeing maintenance needs in machinery, the predictive power of AI provides a competitive edge by reducing uncertainty and enhancing decision-making processes.
Data Privacy Concerns
Artificial intelligence and deep learning systems are increasingly reliant on vast datasets to enhance their accuracy and functionality. However, this dependency raises significant data privacy concerns. As these technologies require extensive personal and sensitive information to train their algorithms, the risk of data breaches and misuse becomes more pronounced. The collection and storage of such large volumes of data can inadvertently expose individuals’ private information, leading to potential privacy violations. Furthermore, without stringent regulations and transparent data handling practices, users may be unaware of how their data is being utilised or shared. This lack of clarity can erode trust in AI systems, highlighting the urgent need for robust privacy safeguards to protect individual rights while advancing technological innovation.
Bias and Fairness Issues
Artificial intelligence and deep learning have brought significant advancements, yet they are not without their challenges. One notable concern is the issue of bias and fairness within AI algorithms. These systems learn from vast datasets, and if the training data contains biases—whether due to historical inequalities or skewed sampling—the AI can inadvertently perpetuate these biases. This can result in unfair outcomes, particularly in decision-making processes such as hiring, lending, or law enforcement. For instance, if a dataset reflects societal prejudices, an AI model may produce discriminatory results against certain groups. Addressing these issues requires careful consideration of data sources and the implementation of strategies to detect and mitigate bias, ensuring that AI technologies contribute positively to society by promoting fairness and equality.
Lack of Transparency
One of the notable drawbacks of artificial intelligence and deep learning is the lack of transparency inherent in their operation. Often referred to as “black boxes,” these models can be exceedingly complex, making it difficult for even experts to discern how they arrive at specific conclusions or decisions. This opacity raises significant concerns, particularly in critical applications such as healthcare, finance, and law enforcement, where understanding the rationale behind a decision is crucial. The inability to interpret these processes not only hampers trust among users but also poses challenges in debugging and improving model performance. As AI systems become more integrated into everyday life, addressing this lack of transparency becomes increasingly important to ensure accountability and reliability.
Dependency on Data Quality
Artificial intelligence and deep learning systems are intrinsically dependent on the quality and diversity of the data they are trained on. This dependency poses a significant challenge, as the accuracy and reliability of AI models are directly influenced by the input data. If the training data is biased, incomplete, or unrepresentative of real-world scenarios, it can lead to skewed results and unreliable predictions. This limitation underscores the importance of curating high-quality datasets that encompass a wide range of scenarios and perspectives. Without such comprehensive data, AI systems may struggle to perform effectively across different contexts, potentially leading to erroneous conclusions and perpetuating existing biases. As a result, ensuring robust data quality is paramount for developing trustworthy AI applications.
Ethical Dilemmas
As artificial intelligence and deep learning become more ingrained in societal structures, they bring with them a host of ethical dilemmas that demand careful consideration. In critical areas such as healthcare, law enforcement, and finance, the deployment of AI systems raises questions about fairness, accountability, and transparency. For instance, in healthcare, AI-driven diagnostics must ensure unbiased treatment across diverse populations. In law enforcement, the use of AI for surveillance or predictive policing can lead to privacy infringements and reinforce existing biases. Similarly, in finance, algorithmic decision-making can impact creditworthiness assessments and access to financial services. As these technologies continue to evolve, it is imperative that ethical frameworks are established to guide their development and application, ensuring they serve humanity equitably and justly without compromising individual rights or societal values.
