Exploring the Depths of Artificial Intelligence Through Machine Learning and Deep Learning
Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning: Understanding the Differences and Connections
The fields of Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL) are often used interchangeably, but they refer to distinct concepts within the realm of computer science. Understanding the differences and connections between these terms is crucial for anyone interested in the technological advancements shaping our world.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is a broad field of computer science focused on creating systems capable of performing tasks that would typically require human intelligence. These tasks include problem-solving, understanding natural language, recognising patterns, and making decisions.
The idea of AI dates back to ancient times with myths and stories about artificial beings endowed with intelligence. However, modern AI began to take shape in the mid-20th century with the advent of computers. Today, AI encompasses various subfields such as robotics, natural language processing (NLP), expert systems, and more.
Machine Learning
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that focuses on developing algorithms that allow computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed. ML enables systems to identify patterns within large datasets and make predictions or decisions based on those patterns.
The core idea behind ML is that by exposing a model to vast amounts of data, it can learn underlying structures and relationships within that data. This learning process involves training models using various techniques such as supervised learning, unsupervised learning, semi-supervised learning, and reinforcement learning.
Deep Learning
Deep Learning, a subset of machine learning inspired by the structure and function of the human brain’s neural networks, focuses on algorithms known as artificial neural networks (ANNs). These networks consist of layers of interconnected nodes or “neurons,” which work together to process information.
The “deep” in deep learning refers to the use of multiple layers in these neural networks. Each layer extracts progressively more abstract features from the input data. For example, in image recognition tasks, initial layers might detect edges or simple shapes while deeper layers recognise complex objects such as faces or animals.
Deep learning has revolutionised many fields by achieving state-of-the-art results in areas like computer vision (e.g., image classification), natural language processing (e.g., language translation), speech recognition (e.g., voice assistants), and more.
The Interconnections
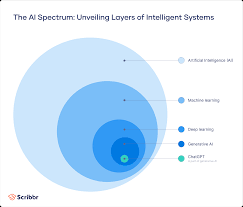
The relationship between AI, ML, and DL can be visualised as concentric circles with AI encompassing both ML and DL:
- AI: The broadest concept encompassing any technique enabling machines to mimic human intelligence.
- ML: A subset within AI focusing on algorithms that allow machines to learn from data without explicit programming.
- DL: A further subset within ML using multi-layered neural networks for advanced pattern recognition tasks.
The Future Impact
The advancements in AI technologies have already begun transforming industries ranging from healthcare (e.g., diagnostic tools) to finance (e.g., fraud detection) to transportation (e.g., autonomous vehicles). As research continues pushing boundaries forward at an unprecedented pace—thanks largely due increasing computational power availability—the potential applications seem limitless!
Mosescore.eu aims at demystifying these complex yet fascinating areas so everyone can understand how they’re shaping our present—and future—worlds alike! Join us exploring this exciting journey into realms where science fiction becomes reality every day!
Understanding Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning: Answers to 7 Common Questions
- What is artificial intelligence?
- How does machine learning differ from artificial intelligence?
- What are the applications of deep learning in today’s world?
- Can you explain the concept of neural networks in machine learning?
- What role does data play in training machine learning models?
- How are artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning related?
- What ethical considerations should be taken into account when developing AI technologies?
What is artificial intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are designed to think and act like humans. This encompasses a wide range of capabilities, from problem-solving and learning to understanding natural language and recognising patterns. AI systems are built to perform tasks that typically require human cognitive functions, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation. By leveraging advanced algorithms and vast amounts of data, AI can adapt to new inputs and improve over time, making it an essential component in various modern technologies from autonomous vehicles to personalised recommendations on streaming services.
How does machine learning differ from artificial intelligence?
Machine learning differs from artificial intelligence in that it is a specific subset within the broader field of AI. While artificial intelligence encompasses any technique that enables machines to mimic human intelligence, such as problem-solving, understanding natural language, and decision-making, machine learning focuses specifically on the development of algorithms that allow computers to learn from and make predictions based on data. In essence, machine learning provides the tools and methods for systems to improve their performance over time through experience without being explicitly programmed for each task. Therefore, while all machine learning is a form of AI, not all AI involves machine learning.
What are the applications of deep learning in today’s world?
One frequently asked question in the realm of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning is: “What are the applications of deep learning in today’s world?” Deep learning, a subset of machine learning inspired by the human brain’s neural networks, has found diverse applications across various industries. In today’s world, deep learning is revolutionising fields such as computer vision (e.g., image recognition), natural language processing (e.g., language translation), speech recognition (e.g., voice assistants), autonomous vehicles, healthcare diagnostics, finance (e.g., fraud detection), and more. Its ability to extract complex patterns from vast amounts of data has enabled breakthroughs in tasks that were once considered challenging for traditional algorithms. The widespread adoption of deep learning showcases its transformative impact on modern technology and society.
Can you explain the concept of neural networks in machine learning?
Neural networks are a fundamental concept in machine learning, particularly within the subset of deep learning. Inspired by the structure and function of the human brain, neural networks consist of layers of interconnected nodes or “neurons,” which process data by passing it through these layers. Each neuron receives input, processes it using a set of weights and biases, and then passes the output to the next layer through an activation function. This layered architecture allows neural networks to learn complex patterns and representations from large datasets. By adjusting the weights and biases during training, neural networks can improve their performance on tasks such as image recognition, natural language processing, and predictive analytics. The depth and complexity of these networks enable them to excel at tasks that traditional machine learning algorithms might struggle with, making them a powerful tool in modern AI applications.
What role does data play in training machine learning models?
Understanding the role of data in training machine learning models is crucial for grasping the essence of artificial intelligence. Data serves as the foundation upon which machine learning models are built and refined. It acts as the fuel that powers the learning process, allowing algorithms to identify patterns, make predictions, and improve their performance over time. The quality, quantity, and relevance of data directly impact the accuracy and effectiveness of machine learning models. Without sufficient and high-quality data, these models may struggle to generalise well or produce meaningful insights. Therefore, data plays a pivotal role in shaping the success and capabilities of machine learning systems within the broader landscape of artificial intelligence.
How are artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning related?
One frequently asked question in the realm of artificial intelligence is: “How are artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning related?” These three concepts are intricately connected within the field of computer science. Artificial intelligence serves as the overarching concept, encompassing machine learning as a subset that focuses on algorithms enabling machines to learn from data. Deep learning, in turn, falls under the umbrella of machine learning, employing multi-layered neural networks to achieve advanced pattern recognition tasks. Understanding these relationships is key to appreciating how these technologies work together to drive innovation and shape the future of AI-powered solutions.
What ethical considerations should be taken into account when developing AI technologies?
When developing AI technologies, several ethical considerations must be taken into account to ensure responsible and fair use. Firstly, issues of bias and fairness are paramount; AI systems should be designed to avoid perpetuating or amplifying existing biases in data, which can lead to unfair treatment of individuals or groups. Transparency is also crucial—developers should strive to make AI decision-making processes understandable and explainable to users. Privacy concerns must be addressed by implementing robust data protection measures to safeguard personal information. Additionally, the potential for job displacement due to automation raises questions about the societal impact of AI, necessitating strategies for workforce transition and reskilling. Finally, accountability mechanisms should be established so that there is a clear understanding of who is responsible when AI systems fail or cause harm. By considering these ethical aspects, developers can create AI technologies that are not only innovative but also socially responsible and beneficial for all.
