Exploring the Intersection of AI, ML, and Deep Learning: A Comprehensive Overview
AI, ML and Deep Learning: A Comprehensive Guide
The realms of Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning are rapidly evolving, transforming the way we interact with technology. These terms are often used interchangeably, but they represent distinct concepts within the field of data science. This article aims to elucidate the differences and interconnections between AI, ML, and Deep Learning.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think like humans and mimic their actions. The term can also be applied to any machine that exhibits traits associated with a human mind such as learning and problem-solving.
AI can be classified into two categories:
- Narrow AI: This type of AI is designed to perform a narrow task (e.g., facial recognition or internet searches).
- General AI: This type of AI possesses the ability to perform any intellectual task that a human can do.
Understanding Machine Learning
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that involves the use of algorithms and statistical models to enable computers to improve their performance on a specific task through experience. Unlike traditional programming where explicit instructions are given for every action, ML allows systems to learn from data patterns.
The primary types of Machine Learning include:
- Supervised Learning: The model is trained on labelled data.
- Unsupervised Learning: The model identifies patterns in unlabelled data.
- Semi-supervised Learning: Combines both labelled and unlabelled data for training.
- Reinforcement Learning: The model learns by receiving rewards or penalties based on its actions.
The Role of Deep Learning
Deep Learning is a specialised subset of Machine Learning involving neural networks with many layers—hence the term “deep”. These neural networks attempt to simulate the behaviour of the human brain in processing data for tasks such as image recognition, speech recognition, and language translation.
The key components of Deep Learning include:
- Neural Networks: Structures composed of layers that process input data in complex ways through interconnected nodes (neurons).
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Primarily used for image processing tasks.
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): Suitable for sequential data like time series or natural language processing.
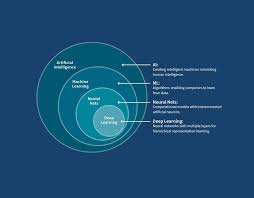
The Interconnection Between AI, ML, and Deep Learning
The relationship between these technologies can be visualised as concentric circles. At the core lies Deep Learning as a subset within Machine Learning, which itself resides within the broader scope of Artificial Intelligence. Each layer builds upon its predecessor:
- A broad goal: Artificial Intelligence aims to create intelligent systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence.
- A focused approach: Machine learning provides methods by which machines can learn from past experiences without being explicitly programmed for each specific task.
- A specialised technique: Deep learning leverages complex neural networks designed to mimic human brain activity for intricate pattern recognition tasks.
The Future Impact on Society
The advancements in AI, ML, and Deep Learning hold tremendous potential across various industries including healthcare, finance, transportation, and entertainment. From autonomous vehicles navigating our roads safely to predictive analytics revolutionising medical diagnostics—these technologies promise unprecedented improvements in efficiency and innovation.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the realms of Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL) represent a pivotal advancement in modern technology.
These fields encompass an array &&&;of methodologies &;and applications &;that have transformed how we interact with machines &;and process information.&
<p></body></html>
