Exploring the Intersection of Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning
Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning: Understanding the Differences
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, terms like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and deep learning (DL) are frequently used. While they are often mentioned together and sometimes interchangeably, each represents a distinct area of technology with its own unique characteristics and applications. This article aims to clarify these differences and provide a comprehensive understanding of each term.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence, commonly referred to as AI, is the broadest concept among the three. It encompasses any technique that enables computers to mimic human intelligence. AI can be divided into two main categories:
- Narrow AI: Also known as weak AI, this type focuses on performing a specific task or set of tasks. Examples include virtual assistants like Siri or Alexa, recommendation systems on streaming services, and chatbots.
- General AI: Also known as strong AI or AGI (Artificial General Intelligence), this type aims to perform any intellectual task that a human can do. General AI remains largely theoretical and is a subject of ongoing research.
Machine Learning
Machine Learning, a subset of AI, involves the development of algorithms that allow computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. The primary goal is to enable machines to make predictions or decisions based on data inputs. Machine learning can be categorised into three main types:
- Supervised Learning: In this approach, the algorithm is trained on labelled data—data that includes both input variables and the corresponding output variables. Examples include spam detection in emails and image recognition.
- Unsupervised Learning: Here, the algorithm is given data without explicit instructions on what to do with it. The system tries to identify patterns or structures within the data. Common applications include clustering customers based on purchasing behaviour.
- Semi-Supervised Learning: This method uses a mix of labelled and unlabelled data for training purposes.
Deep Learning
Deep Learning, a specialised subset of machine learning, employs neural networks with many layers—hence the term “deep”. These deep neural networks are capable of automatically discovering representations from raw data without manual feature engineering. Deep learning has revolutionised fields such as computer vision, natural language processing (NLP), and speech recognition.
The most common types of neural networks used in deep learning include:
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Primarily used for image-related tasks such as object detection and facial recognition.
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): Ideal for sequence-based tasks such as language translation and time series forecasting.
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs):: Used for generating new content like images or music by pitting two neural networks against each other.
The Interconnection Between AI, ML, and DL
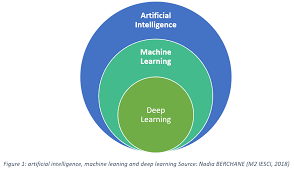
The relationship between these three concepts can be visualised as concentric circles: deep learning sits inside machine learning which in turn sits inside artificial intelligence. In essence:
- Aritifical Intelligence (AI) is the overarching concept that encompasses both machine learning and deep learning.
- .
<
Understanding AI: Key Questions on Machine Learning and Deep Learning
- What is machine learning in AI?
- What are the 3 domains of AI?
- What is an example of deep learning?
- What is the difference between artificial intelligence and machine learning and deep learning?
- What is the difference between artificial intelligence machine learning and deep learning?
- How is machine learning related to artificial intelligence and deep learning?
- What is difference between AI ML and DL?
What is machine learning in AI?
Machine learning in AI refers to a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on the development of algorithms and statistical models, enabling computers to perform tasks without explicit instructions. Instead, these systems learn from data patterns and make decisions or predictions based on that data. By processing large amounts of information, machine learning algorithms can identify trends, classify data, and even improve their performance over time. This approach is widely used in various applications such as recommendation systems, fraud detection, and autonomous vehicles, making it a cornerstone of modern AI advancements.
What are the 3 domains of AI?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is broadly categorised into three primary domains: Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), and Artificial Superintelligence (ASI). **Artificial Narrow Intelligence**, also known as weak AI, is designed to perform a specific task or a narrow range of tasks, such as language translation or facial recognition. It operates under a limited set of constraints and does not possess general cognitive abilities. **Artificial General Intelligence**, or strong AI, represents machines with the ability to understand, learn, and apply intelligence across a wide range of tasks at a level comparable to human beings. AGI remains largely theoretical and is the subject of extensive research and debate within the field. Lastly, **Artificial Superintelligence** refers to an intelligence that surpasses human capabilities in all aspects, including creativity, problem-solving, and emotional intelligence. ASI is currently speculative and raises significant ethical and existential questions about the future of humanity’s relationship with intelligent machines.
What is an example of deep learning?
An example of deep learning is the application of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) in image recognition. CNNs, a type of deep neural network, have revolutionised the field of computer vision by enabling machines to automatically identify and classify objects within images. Through multiple layers of interconnected neurons, CNNs can learn intricate patterns and features within visual data, allowing for highly accurate image recognition tasks. This technology powers applications such as facial recognition systems, autonomous vehicles, medical imaging analysis, and more, showcasing the remarkable capabilities of deep learning in real-world scenarios.
What is the difference between artificial intelligence and machine learning and deep learning?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the overarching concept that encompasses the creation of systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as decision-making and language understanding. Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI that focuses on the development of algorithms which enable computers to learn from and make predictions based on data. Deep Learning (DL), a further subset within ML, involves the use of neural networks with multiple layers to analyse various factors of data. While AI represents the broad goal of intelligent machines, ML provides the tools to achieve this through data-driven learning, and DL offers advanced techniques for handling complex data structures and achieving high levels of accuracy in tasks like image and speech recognition.
What is the difference between artificial intelligence machine learning and deep learning?
The difference between artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and deep learning (DL) lies in their scope and complexity. AI is the broadest concept, encompassing any technique that enables machines to mimic human intelligence, ranging from simple rule-based systems to complex neural networks. Machine learning is a subset of AI that involves training algorithms to learn from data and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed. Within ML, deep learning represents a specialised area that uses multi-layered neural networks to automatically discover intricate patterns in large datasets, enabling advanced applications such as image and speech recognition. In essence, while all deep learning is a form of machine learning, not all machine learning qualifies as deep learning, and both fall under the wider umbrella of AI.
How is machine learning related to artificial intelligence and deep learning?
Machine learning serves as a crucial link between artificial intelligence and deep learning, forming a fundamental component in the realm of advanced technologies. While artificial intelligence encompasses a broader scope of mimicking human intelligence through computer systems, machine learning focuses specifically on developing algorithms that enable machines to learn from data without explicit programming. Deep learning, on the other hand, represents a more intricate subset of machine learning that utilises deep neural networks to automatically extract meaningful representations from raw data. Therefore, machine learning acts as the bridge connecting the overarching concept of artificial intelligence with the specialized domain of deep learning, facilitating the progression and application of intelligent technologies in various fields.
What is difference between AI ML and DL?
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL) are interconnected yet distinct fields within the realm of computer science. AI is the broadest concept, referring to any technique that enables machines to mimic human intelligence, encompassing everything from simple rule-based systems to advanced neural networks. Machine Learning is a subset of AI that focuses on developing algorithms allowing computers to learn from data and make decisions or predictions without being explicitly programmed; it includes methods like supervised, unsupervised, and semi-supervised learning. Deep Learning, a specialised subset of ML, involves neural networks with many layers—known as deep neural networks—that automatically discover patterns and representations in large datasets, excelling in tasks such as image recognition and natural language processing. In summary, while AI is the overarching field aiming to replicate human intelligence, ML provides the tools for learning from data, and DL leverages complex neural networks for advanced data analysis.
