Exploring the Synergy of Machine Learning, AI, and Deep Learning
Understanding Machine Learning, AI, and Deep Learning
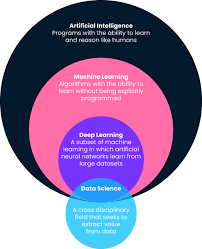
In recent years, terms like machine learning, artificial intelligence (AI), and deep learning have become increasingly prevalent in discussions about technology and its future. While often used interchangeably, these concepts are distinct yet interconnected components of modern computing.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, particularly computer systems. These processes include learning (the acquisition of information and rules for using the information), reasoning (using rules to reach approximate or definite conclusions), and self-correction. AI can be categorised into two types: narrow AI, which is designed for a specific task such as voice recognition or image classification; and general AI, which aims to perform any intellectual task that a human can do.
Machine Learning
Machine Learning, a subset of AI, involves the use of algorithms and statistical models that enable computers to perform tasks without explicit instructions. Instead of being programmed with specific rules to follow, machine learning systems are trained on large datasets and learn from experience. This approach allows them to improve their performance over time as they are exposed to more data.
The power of machine learning lies in its ability to identify patterns and make decisions with minimal human intervention. It is widely used in various applications such as recommendation systems, fraud detection, and predictive analytics.
Deep Learning
Deep Learning, a specialised branch of machine learning, employs neural networks with many layers—hence the term “deep”. These deep neural networks are designed to mimic the way the human brain operates by processing data through multiple layers of neurons.
This method has revolutionised fields such as computer vision, natural language processing, and speech recognition by significantly improving accuracy. Deep learning models require large amounts of data and substantial computational power but have proven highly effective in tasks previously thought too complex for machines.
The Interconnected World of AI Technologies
The relationship between AI, machine learning, and deep learning is hierarchical: deep learning is a subset of machine learning which itself is a subset of artificial intelligence. Together, they form an ecosystem that drives innovation across industries—from healthcare to finance—and transforms how we interact with technology on a daily basis.
The potential applications are vast: self-driving cars use deep learning algorithms for navigation; virtual assistants leverage machine learning for understanding user preferences; while AI-powered diagnostic tools offer unprecedented accuracy in medical imaging.
The Future Outlook
The development in these fields continues at an unprecedented pace. As computational power increases and datasets become more comprehensive, the capabilities of machine learning and deep learning will only expand further. The future promises even more sophisticated applications that will reshape industries globally.
The journey towards fully realised artificial intelligence is ongoing but holds immense promise for enhancing productivity and solving complex challenges facing humanity today.
8 Key Advantages of Machine Learning and Deep Learning: From Enhanced Decision Making to Driving Innovation
- 1. Enhanced Decision Making
- 2. Automation of Tasks
- 3. Personalised Experiences
- 4. Improved Efficiency
- 5. Predictive Analytics
- 6. Advanced Problem Solving
- 7. Scalability
- 8. Innovation Catalyst
Challenges in Machine Learning and Deep Learning: Addressing Data Dependency, Interpretability, Overfitting, Ethical Concerns, Computational Demands, and Generalisation Limitations
- 1. Data Dependency
- 2. Interpretability
- 3. Overfitting
- 4. Ethical Concerns
- 5. Computational Resources
- 6. Lack of Generalisation
1. Enhanced Decision Making
One significant advantage of machine learning, AI, and deep learning is their ability to enhance decision-making processes. By utilising sophisticated algorithms, these technologies can efficiently analyse enormous datasets to derive valuable insights and make well-informed decisions promptly and accurately. This capability enables businesses and organisations to leverage data-driven approaches for strategic planning, resource allocation, risk assessment, and more, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and effectiveness in various domains.
2. Automation of Tasks
One significant advantage of machine learning, AI, and deep learning is their ability to automate repetitive tasks, allowing employees to redirect their time and energy towards strategic and creative endeavours. By harnessing these technologies, organisations can streamline operations, increase efficiency, and unlock the potential for innovation in the workforce. Automation not only enhances productivity but also empowers employees to engage in higher-value activities that contribute to the overall growth and success of the business.
3. Personalised Experiences
One of the significant advantages of machine learning and deep learning within AI systems is their ability to create personalised experiences tailored to individual user preferences. By analysing vast amounts of data, AI-driven systems can discern patterns and make accurate predictions about user behaviour and preferences. This capability allows businesses to offer customised recommendations, content, and services that resonate with each user on a personal level. As a result, customers enjoy a more engaging and satisfying experience, which not only enhances customer satisfaction but also fosters loyalty and long-term relationships. Whether it’s personalised shopping suggestions, curated playlists, or targeted advertising, the personalisation enabled by AI technologies transforms how users interact with digital platforms, making their experiences more relevant and enjoyable.
4. Improved Efficiency
One significant advantage of machine learning, AI, and deep learning is their ability to enhance efficiency within various processes and workflows. By utilising machine learning algorithms, organisations can streamline operations, identify patterns, and make data-driven decisions that result in improved efficiency and substantial cost savings. This optimisation not only boosts productivity but also allows businesses to allocate resources more effectively, ultimately leading to enhanced performance and competitiveness in the market.
5. Predictive Analytics
One significant advantage of deep learning in the realm of artificial intelligence is its capability for predictive analytics. By utilising historical data, deep learning models can analyse patterns and trends to forecast future outcomes. This predictive power empowers businesses to make proactive decisions, anticipate market shifts, and optimise strategies for better results. Harnessing the predictive capabilities of deep learning enables organisations to stay ahead of the curve and adapt swiftly to changing circumstances, ultimately enhancing their competitiveness and success in the dynamic business landscape.
6. Advanced Problem Solving
Machine learning, AI, and deep learning have revolutionised advanced problem-solving by tackling complex issues that traditional computing methods struggle to address. These technologies are capable of processing vast amounts of data, identifying intricate patterns, and making data-driven decisions with remarkable accuracy. By leveraging sophisticated algorithms and neural networks, AI systems can analyse multifaceted problems across various domains, such as healthcare, finance, and engineering. This capability allows for the optimisation of processes, enhancement of predictive models, and development of innovative solutions that were previously unattainable. As a result, AI technologies empower industries to overcome challenges with unprecedented efficiency and insight.
7. Scalability
One notable advantage of machine learning, AI, and deep learning is their scalability. These systems have the capability to seamlessly expand and manage vast amounts of data without sacrificing performance or accuracy. This scalability feature allows organisations to process and analyse extensive datasets efficiently, enabling them to derive valuable insights and make informed decisions on a large scale. As businesses and industries continue to generate increasing amounts of data, the scalability of machine learning technologies plays a crucial role in unlocking their full potential and driving innovation across various sectors.
8. Innovation Catalyst
An undeniable pro of AI, machine learning, and deep learning is their role as an Innovation Catalyst. These technologies are at the forefront of driving innovation across industries by facilitating the creation of cutting-edge solutions. By harnessing the power of data analysis, pattern recognition, and neural networks, businesses can develop revolutionary products and services that push the boundaries of what is possible, paving the way for a future where technology plays a central role in shaping progress and success.
1. Data Dependency
One significant drawback of machine learning, AI, and deep learning technologies is their heavy reliance on vast quantities of precise and reliable data for effective training. Acquiring such high-quality data can be a challenging and resource-intensive process, often involving significant time and financial investments. This data dependency poses a barrier to the widespread adoption and implementation of these technologies, limiting their potential impact in various industries and applications.
2. Interpretability
One significant drawback of deep learning, and machine learning models in general, is their lack of interpretability. Deep learning models, in particular, are often referred to as ‘black boxes’ because of their intricate structures, which can make it difficult to understand the reasoning behind their decisions. This lack of transparency poses a challenge when trying to interpret how these models arrive at specific conclusions or predictions, raising concerns about accountability and trust in the decision-making process.
3. Overfitting
One significant drawback of machine learning, AI, and deep learning is the issue of overfitting. This occurs when algorithms become too tailored to the training data, resulting in high performance during training but poor generalisation to new, unseen data. Overfitting can lead to inaccurate predictions and compromises the reliability and effectiveness of the models in real-world applications. It poses a challenge in ensuring that machine learning systems can adapt and perform well beyond the data they were initially trained on.
4. Ethical Concerns
One significant concern surrounding machine learning and deep learning in AI is the potential for ethical issues, particularly regarding bias. AI systems learn from vast datasets, and if these datasets contain biases—whether related to race, gender, socioeconomic status, or other factors—the AI can inadvertently perpetuate these biases in its decision-making processes. This can lead to discriminatory outcomes, such as unfair treatment in hiring practices or biased loan approvals. Without careful monitoring and management, AI systems may reinforce existing societal inequalities rather than alleviate them. It is crucial for developers and organisations to implement rigorous checks and balances to ensure that AI applications are fair and ethical, promoting transparency and accountability throughout the development process.
5. Computational Resources
One significant drawback of deep learning, machine learning, and artificial intelligence is the heavy demand for computational resources. Deep learning models, in particular, necessitate substantial computational power for both training and inference tasks. This high requirement can pose a challenge for individuals or organisations with limited resources, hindering their ability to fully leverage the potential of these advanced technologies. The cost associated with acquiring and maintaining the necessary hardware and infrastructure can act as a barrier to entry, limiting access to these powerful tools for innovation and problem-solving.
6. Lack of Generalisation
One significant drawback of machine learning, AI, and deep learning is the challenge of generalisation. Although these models demonstrate remarkable performance in tasks they are trained for, they often face difficulties when applied to unfamiliar or unanticipated situations without additional adjustments. This lack of generalisation capability can limit their effectiveness in real-world scenarios where adaptability and flexibility are crucial. Fine-tuning and continuous refinement are necessary to enhance the models’ ability to handle diverse and evolving challenges beyond their initial training scope.
