The Impact of AI on Jobs and Society: A Transformative Force
The Impact of AI on Jobs and Society
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the way we live and work, bringing both opportunities and challenges to the forefront. As AI technologies continue to advance, they are reshaping industries, creating new job roles, and altering societal dynamics.
AI and the Job Market
The impact of AI on the job market is a topic of significant debate. On one hand, AI has the potential to automate routine tasks, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. This automation can result in the displacement of certain jobs, particularly those involving repetitive tasks. For example, manufacturing jobs that rely heavily on manual labour are increasingly being replaced by robotic systems.
However, AI also creates new opportunities. The demand for skilled professionals who can develop, implement, and maintain AI systems is growing rapidly. Roles such as data scientists, machine learning engineers, and AI ethicists are becoming increasingly important as organisations seek to harness the power of AI.
Transforming Industries
AI is revolutionising various industries by enabling smarter decision-making processes and enhancing customer experiences. In healthcare, AI algorithms assist in diagnosing diseases with greater accuracy than ever before. In finance, AI-driven analytics help predict market trends and manage risks more effectively.
The retail sector is also benefiting from AI through personalised shopping experiences powered by recommendation engines. These engines analyse consumer behaviour to provide tailored product suggestions that enhance customer satisfaction.
Societal Implications
Beyond its impact on jobs and industries, AI poses broader societal implications that require careful consideration. Privacy concerns arise as AI systems collect vast amounts of data for analysis. Ensuring data security and protecting individuals’ privacy rights are paramount in an age where personal information is a valuable commodity.
Moreover, ethical considerations surrounding bias in AI algorithms have come to light. If not addressed properly, these biases can perpetuate existing inequalities within society. Developing fair and unbiased algorithms is crucial to ensuring that all individuals benefit equally from technological advancements.
The Path Forward
Navigating the impact of AI on jobs and society requires a balanced approach that embraces innovation while addressing potential challenges head-on. Policymakers must work collaboratively with industry leaders to create frameworks that support workforce transition programmes for displaced workers while fostering education initiatives focused on digital skills development.
Furthermore, transparency in algorithmic decision-making processes should be encouraged so that individuals understand how their data is used by organisations employing AI technologies.
Conclusion
The rise of artificial intelligence presents both exciting possibilities for progress as well as complex challenges for our societies worldwide; however it offers an opportunity for us all – governments businesses academia civil society alike -to shape this transformation into one which benefits everyone equitably across generations present future alike!
Navigating the Impact of AI on Jobs and Society: Essential Strategies and Considerations
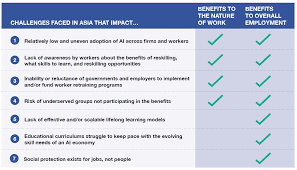
- Upskilling and reskilling workers is essential to adapt to the changing job landscape due to AI.
- AI can create new job opportunities in fields like data science, machine learning, and AI development.
- It is important for policymakers to create regulations that ensure fair treatment of workers affected by AI automation.
- AI can improve efficiency in many industries but may also lead to displacement of certain jobs that are routine or repetitive.
- Ethical considerations must be taken into account when developing and deploying AI technologies to mitigate negative impacts on society.
- ‘Human-in-the-loop’ approaches where humans work alongside AI systems can help maintain accountability and oversight in critical decision-making processes.
Upskilling and reskilling workers is essential to adapt to the changing job landscape due to AI.
As AI continues to reshape industries and redefine job roles, upskilling and reskilling workers have become essential strategies for adapting to the evolving job landscape. The integration of AI technologies often leads to the automation of routine tasks, which can displace certain jobs while simultaneously creating demand for new skills. By investing in upskilling and reskilling initiatives, individuals can enhance their existing capabilities or acquire new competencies that align with emerging roles in the AI-driven economy. This not only helps workers remain competitive in the job market but also empowers them to take advantage of opportunities in sectors experiencing growth due to technological advancements. For businesses, fostering a culture of continuous learning ensures a more agile and adaptable workforce, capable of navigating the complexities introduced by AI innovations. Ultimately, prioritising education and training is crucial for both individuals and organisations to thrive in an era where artificial intelligence plays an increasingly significant role.
AI can create new job opportunities in fields like data science, machine learning, and AI development.
Artificial Intelligence is not only reshaping existing roles but also paving the way for new job opportunities in burgeoning fields such as data science, machine learning, and AI development. As organisations increasingly adopt AI technologies, there is a growing demand for skilled professionals who can design, implement, and manage these systems. This has led to the creation of specialised roles that focus on developing algorithms, analysing large datasets, and ensuring the ethical deployment of AI solutions. Consequently, while some traditional jobs may be at risk of automation, the rise of AI is simultaneously generating a wealth of new career paths that require advanced technical expertise and innovative thinking. This shift underscores the importance of education and training programmes that equip individuals with the necessary skills to thrive in an AI-driven landscape.
It is important for policymakers to create regulations that ensure fair treatment of workers affected by AI automation.
As AI automation continues to transform industries, it is crucial for policymakers to establish regulations that safeguard the fair treatment of workers impacted by these technological advancements. Such regulations should focus on providing adequate support for workforce transition, including retraining programmes and job placement services, to help displaced workers adapt to new roles in the evolving job market. Additionally, policies must ensure that employment rights are protected and that workers receive fair compensation and benefits during periods of transition. By fostering an equitable environment, policymakers can help mitigate the potential negative effects of AI automation on employment while promoting a more inclusive and resilient economy.
AI can improve efficiency in many industries but may also lead to displacement of certain jobs that are routine or repetitive.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has the potential to significantly enhance efficiency across a range of industries by automating tasks that are routine or repetitive. This technological advancement allows businesses to streamline operations, reduce errors, and increase productivity, ultimately leading to improved service delivery and cost savings. However, this shift towards automation also poses challenges, particularly in the form of job displacement for workers whose roles primarily involve repetitive tasks. As AI continues to evolve, it is crucial for industries and policymakers to consider strategies for workforce transition, including reskilling and upskilling initiatives, to ensure that employees can adapt to new roles within an increasingly automated environment. Balancing the benefits of AI-driven efficiency with the need for sustainable employment opportunities will be key in navigating the future landscape of work.
Ethical considerations must be taken into account when developing and deploying AI technologies to mitigate negative impacts on society.
When developing and deploying AI technologies, it is crucial to take ethical considerations into account to mitigate potential negative impacts on society. As AI systems become more integrated into daily life, they hold the power to significantly influence various aspects of human existence, from employment to privacy. Without careful consideration, AI can perpetuate biases, infringe on individual rights, and exacerbate existing inequalities. Therefore, developers and policymakers must prioritise transparency and fairness in AI algorithms to ensure they serve the broader good. By embedding ethical principles into the design and implementation phases, society can harness the benefits of AI while minimising harm and fostering trust in these transformative technologies.
‘Human-in-the-loop’ approaches where humans work alongside AI systems can help maintain accountability and oversight in critical decision-making processes.
The integration of ‘human-in-the-loop’ approaches, where humans collaborate with AI systems, plays a crucial role in maintaining accountability and oversight in critical decision-making processes. By ensuring that human judgement remains a key component of AI-driven operations, organisations can mitigate risks associated with automated decisions. This approach allows for the combination of human intuition and ethical considerations with the efficiency and analytical power of AI. It ensures that decisions, particularly those affecting people’s lives or involving complex ethical dilemmas, are made with a balanced perspective that values both technological advancement and human insight. As a result, ‘human-in-the-loop’ systems help build trust in AI technologies by providing transparency and reducing the likelihood of errors or biases inherent in fully automated processes.
