Unravelling the Intricacies of Neurons: A Journey into the Brain’s Building Blocks
The Fascinating World of Neurons
Neurons are the building blocks of the nervous system, playing a crucial role in transmitting information throughout the body. These specialised cells are responsible for processing and transmitting electrical and chemical signals, enabling communication within the brain and between the brain and other parts of the body.
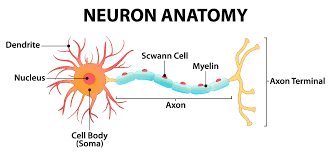
Each neuron consists of a cell body, dendrites, and an axon. The cell body contains the nucleus and other organelles essential for the neuron’s functions. Dendrites receive signals from other neurons or sensory receptors, while the axon carries signals away from the cell body to other neurons or effector cells.
Neurons communicate with each other through synapses, which are junctions where signals are transmitted from one neuron to another. Neurotransmitters released at these synapses play a vital role in signal transmission and processing.
The complexity and diversity of neurons allow for a wide range of functions within the nervous system. Sensory neurons transmit signals from sensory organs to the brain, motor neurons control muscle movements, and interneurons facilitate communication between different parts of the nervous system.
Research into neurons has provided valuable insights into brain function, learning, memory, and various neurological disorders. Understanding how neurons work is essential for advancing our knowledge of the brain and developing treatments for neurological conditions.
In conclusion, neurons are remarkable cells that form intricate networks responsible for our thoughts, actions, and senses. Their structure and function continue to intrigue scientists and inspire further exploration into the mysteries of the human brain.
4.
- Is a neuron a brain cell?
- What are the three types of neurons?
- What is neuron and its types and function?
- What do neurons do in the cell body?
Is a neuron a brain cell?
A common question that arises is whether a neuron is considered a brain cell. In essence, neurons are indeed brain cells, but they are not the only type of cells found in the brain. Neurons are specialised cells that transmit electrical and chemical signals within the nervous system, including the brain. These cells play a fundamental role in processing information and facilitating communication between different parts of the brain and the rest of the body. While neurons are crucial for brain function, other types of cells, such as glial cells, also contribute to supporting and maintaining the overall health and function of the brain.
What are the three types of neurons?
There are three main types of neurons in the nervous system: sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Sensory neurons are responsible for transmitting sensory information from the body’s sensory organs to the brain. Motor neurons, on the other hand, convey signals from the brain to muscles and glands, controlling movement and physiological responses. Interneurons act as connectors within the nervous system, facilitating communication between sensory and motor neurons. Each type of neuron plays a crucial role in processing information and coordinating responses throughout the body’s intricate network of neural pathways.
What is neuron and its types and function?
The neuron is a fundamental cell in the nervous system responsible for transmitting electrical and chemical signals. Neurons consist of a cell body, dendrites, and an axon, with each part playing a crucial role in signal transmission. There are three main types of neurons: sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Sensory neurons transmit signals from sensory organs to the brain, motor neurons control muscle movements, and interneurons facilitate communication between different parts of the nervous system. These diverse types of neurons work together to enable functions such as movement, sensation, and information processing within the body.
What do neurons do in the cell body?
In the cell body of a neuron, also known as the soma, essential functions crucial to the neuron’s operation take place. The cell body houses the nucleus, which contains genetic material and controls cellular activities. Additionally, various organelles within the cell body play vital roles in protein synthesis, energy production, and overall cellular maintenance. Neurons integrate incoming signals received from dendrites in the cell body, where these signals are processed and transformed into electrical impulses that travel along the axon for communication with other neurons or effector cells. Thus, the cell body of a neuron serves as a control centre where information is processed and coordinated before being transmitted to other parts of the nervous system.
