Unveiling the Power of U-Net in Deep Learning: A Comprehensive Exploration
Exploring U-Net Deep Learning: A Powerful Tool in Image Segmentation
U-Net is a convolutional neural network architecture that has gained popularity in the field of deep learning, particularly for tasks related to image segmentation. Developed by researchers at the Computer Science Department of the University of Freiburg, U-Net is known for its effectiveness in biomedical image analysis, satellite image segmentation, and more.
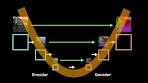
The unique structure of U-Net consists of a contracting path to capture context and a symmetric expanding path for precise localization. This architecture allows U-Net to produce accurate segmentation masks even with limited training data.
One key feature of U-Net is its skip connections, which enable the network to retain fine-grained details during the upsampling process. This helps prevent information loss and improves the accuracy of segmentation results.
U-Net has been successfully applied in various domains, such as medical imaging for tumour detection, cell segmentation in microscopy images, and semantic segmentation in autonomous driving systems. Its versatility and robust performance make it a valuable tool for researchers and practitioners working on image analysis tasks.
As deep learning continues to advance, U-Net remains at the forefront of image segmentation techniques, offering state-of-the-art results and pushing the boundaries of what is possible in computer vision applications.
In conclusion, U-Net deep learning represents a powerful approach to image segmentation, providing researchers with a reliable tool for extracting meaningful information from complex visual data. Its innovative design and impressive performance make it a valuable asset in the field of deep learning and computer vision.
Understanding U-Net: Advantages, Disadvantages, and Comparisons with CNN and UNet++ in Deep Learning
- Why is U-Net better than CNN?
- What is U-Net deep learning?
- What are the disadvantages of U-Net?
- What is the difference between CNN and U-Net?
- What is U-Net in deep learning?
- Is UNet++ better than U-Net?
Why is U-Net better than CNN?
When comparing U-Net to traditional Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), one of the key reasons why U-Net stands out is its unique architecture tailored for image segmentation tasks. While CNNs are powerful for general image classification, U-Net’s design, with skip connections and an expansive path, allows it to capture intricate details and spatial information essential for precise segmentation. The skip connections in U-Net facilitate the flow of fine-grained features across different network layers, enabling better localization accuracy and mitigating the risk of information loss during upsampling. This distinctive feature makes U-Net particularly effective in tasks requiring pixel-level segmentation, such as medical imaging and satellite image analysis. Overall, U-Net’s specialised architecture and emphasis on preserving spatial information make it a preferred choice over CNNs for image segmentation applications where detailed segmentation accuracy is crucial.
What is U-Net deep learning?
U-Net deep learning is a convolutional neural network architecture that has garnered significant attention in the realm of image segmentation tasks. Developed by researchers at the University of Freiburg, U-Net is renowned for its effectiveness in various applications, particularly in biomedical image analysis and satellite image segmentation. Its distinctive design comprises a contracting path for contextual information capture and an expanding path for precise localization, with skip connections that help preserve fine details during upsampling. This unique structure enables U-Net to generate accurate segmentation masks, making it a valuable tool for researchers and practitioners seeking robust solutions for complex image analysis challenges.
What are the disadvantages of U-Net?
When considering the disadvantages of U-Net in deep learning, one common concern is its tendency to overfit when trained on small datasets. Due to its complex architecture and large number of parameters, U-Net may struggle to generalize well to unseen data if not enough diverse examples are provided during training. Additionally, the computational resources required to train U-Net can be significant, making it challenging for researchers with limited access to high-performance computing systems. Despite these drawbacks, researchers continue to explore ways to mitigate these limitations and enhance the performance of U-Net for various image segmentation tasks.
What is the difference between CNN and U-Net?
The key difference between Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and U-Net lies in their architecture and application. While CNNs are commonly used for various tasks such as image classification and object detection, U-Net is specifically designed for image segmentation. Unlike traditional CNNs, U-Net incorporates skip connections that allow it to capture both local features and global context effectively, making it ideal for tasks that require precise localization, such as medical image analysis. This unique design of U-Net enables it to produce accurate segmentation masks by combining the strengths of both the contracting and expanding paths in its architecture.
What is U-Net in deep learning?
In the realm of deep learning, U-Net is a convolutional neural network architecture that has garnered significant attention and acclaim for its exceptional capabilities in image segmentation tasks. Developed by researchers at the University of Freiburg, U-Net features a distinctive design comprising a contracting path for contextual information extraction and an expanding path for precise localization, making it particularly effective in tasks requiring accurate segmentation masks. Its incorporation of skip connections enables the preservation of fine details during upsampling, mitigating information loss and enhancing segmentation accuracy. Widely utilised in diverse domains such as medical imaging, microscopy analysis, and autonomous driving systems, U-Net stands as a versatile and powerful tool that continues to push the boundaries of what is achievable in computer vision applications.
Is UNet++ better than U-Net?
The comparison between UNet++ and U-Net is a frequently asked question in the field of deep learning, particularly in image segmentation tasks. While both architectures are based on the original U-Net design, UNet++ introduces additional features such as dense skip connections and nested architectures to improve segmentation accuracy and handle more complex data structures. Some studies have shown that UNet++ can outperform U-Net in certain scenarios by capturing more detailed information and enhancing the network’s ability to learn intricate patterns. However, the choice between UNet++ and U-Net ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the task at hand, as each architecture has its strengths and limitations that should be carefully considered for optimal performance.
